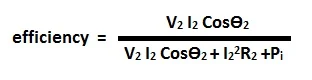What is Transformer?
A transformer is an Electrical static device. it consists of two or more stationary coil which is interlinked by a common magnetic circuit for the purpose of transferring electrical energy from one coil to another. The transfer of electrical energy from one coil to another coil takes place without a change in frequency. The transformer is one of the most efficient machines in the world.
What is Efficiency?
Efficiency is a machine parameter that is used to represent the workability of the machine. it is defined as the ratio of the output of the machine to the input of the machine. it is a unitless and dimensionless quantity. it is represented by a symbol (η) Etta. The efficiency of any machine is always represented in percentages. The efficiency of the transformer is defined as the ratio of Electrical Output power to Electrical Input power.
For a given transformer Input Power = Output Power + Loss
There are two types of loss that occur in the transformer (a) Copper Loss (b) Iron Loss
i.e Loss = Copper Loss + Iron Loss
Then Input Power for Transformer =Output Power + Copper loss + Iron Loss
For a given transformer of power factor CosƟ2 and I2 load Current and V2 Transformer Terminal Voltage
Output Power of Transformer will be given as
Output Power = V2 I2 CosƟ2
Copper loss for a transformer is variable and it totally depends on load current and is given as
I22R2 , Here R2 is Total Equivalent Resistance of Transformer.
Iron loss for a given transformer is almost Constant and it will not vary with load current. Let Iron loss for a given Transformer is Pi
Then Input Power for a given Transformer is
Input power = V2 I2 CosƟ2 + I22R2 +Pi